
Let’s be honest for a second: writing great content feels amazing, doesn’t it? You put your heart into a blog post, you polish every sentence, and you hit “publish” with a touch of pride. But then…No traffic, no comments, no shares. It’s frustrating. I’ve been there, and I know exactly how discouraging it can feel.
Usually, the problem isn’t your writing style or your ideas. The problem is that you’re writing about things people aren’t actually searching for in Google. This is where the magic of keyword research SEO comes into play.
If you’ve been treating SEO (Search Engine Optimization) like a math problem, I’m here to tell you it’s actually much more like a conversation. It’s about listening to what your audience is asking and then providing the best possible answer.
In this guide, we are going to walk through exactly how to master keyword research SEO from scratch. Whether you are a total beginner or just need a refresher, this is your roadmap to getting found online.
Table of Contents
What Exactly is Keyword Research?

Before we discuss about “how-to,” let’s clarify the “what.”
In simple terms, keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing the search terms that people enter into search engines. The goal is to use that data for a specific purpose, usually for search engine optimization (SEO) or general marketing.
When you nail your keyword research SEO strategy, you uncover queries to target, the popularity of these queries, their ranking difficulty, and more. It’s essentially market research. Instead of guessing what your customers want, you look at the data to see exactly what they are typing into the search bar.
Why Is It So Important?
Imagine opening a pizza shop in a town where everyone is influenced to their fitness, but you only sell traditional tasty pizzas. You’d go out of business, right? Content marketing is the same.
You can create the most beautiful article in the world, but if nobody is searching for that topic, Google won’t show it to anyone. Effective keyword research SEO ensures that there is an existing audience for the content you plan to create. It bridges the gap between your brand and the people looking for you
- Also Read: Importance of Email Marketing in 2026
Step 1: Brainstorming Your Keywords

Every great keyword research SEO journey starts with a simple brainstorming session. You don’t need fancy tools for this part—just your brain and maybe a notepad.
Ask yourself: If I were looking for my business/blog, what would I post into Google?
For example, if you run a business selling hiking gear, your seed keywords might look like this:
- Hiking boots
- Camping gear
- Best hiking trails
- Waterproof jackets
Pro Tip: Don’t overthink this. These keywords are likely not to rank for immediately, but they are necessary because you will plug them into tools later to find the hidden tips. This is just the starting process of your keyword research SEO process.
Step 2: Use the Right SEO Tools

Now that you have your seeds, it’s time to expand that list using data. You can’t do effective keyword research SEO based on intuition alone; you need hard numbers.
There are plenty of tools out there, ranging from free to expensive enterprise software. Here are a few favorites:
- Google Keyword Planner: This is free (you just need a Google Ads account). It’s great for finding search volumes and new ideas directly from the source.
- SEMrush or Ahrefs: These are the heavy hitters. They provide incredible depth on keyword difficulty and competitor gaps.
- AnswerThePublic: This tool is fantastic for seeing the questions people are asking around your keywords (e.g., “Which hiking boots are best for snow?”).
When you plug your keywords into these tools, they will spit out hundreds, sometimes thousands, of related keyword ideas. This is where the real keyword research SEO work begins—filtering through the noise to find the gold.
Step 3: Understanding Search Intent
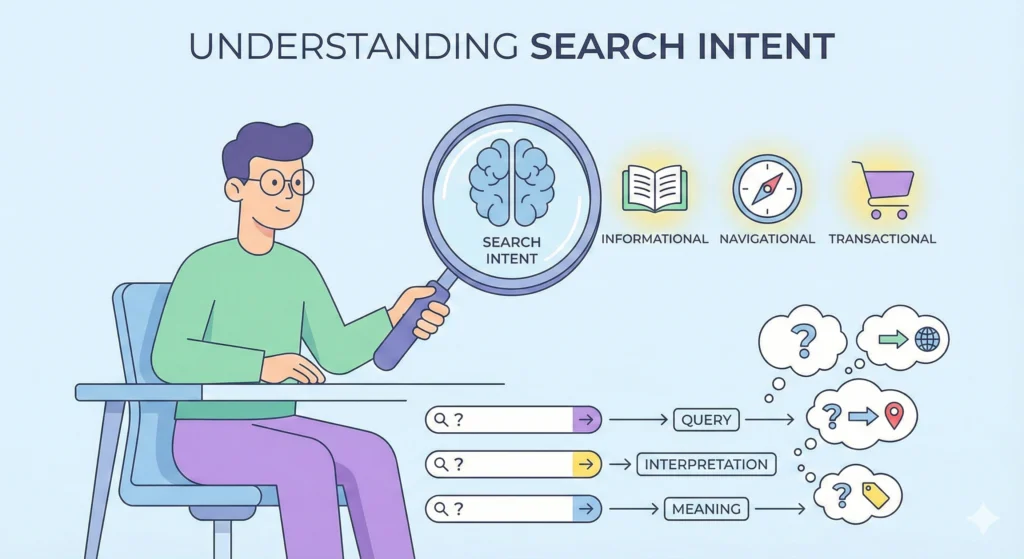
This is the step most beginners skip, and it costs them dearly.
You can find a keyword with high traffic, but if you misunderstand the intent behind it, you will not rank. Google has gotten very smart. It wants to show users exactly what they are looking for, not just a page that contains the matching word.
In the world of keyword research SEO, search intent generally falls into four buckets:
- Informational: The user wants to learn something.
- Example: “How to clean hiking boots”
- Directional: The user is looking for a specific website or page.
- Example: “North Face login”
- Commercial Query: The user is comparing products before buying.
- Example: “Best hiking boots for women 2025”
- Transaction Based: The user is ready to buy right now.
- Example: “Buy waterproof hiking boots size 10”
Why does this matter? Well, if you try to sell a product on a keyword where people are just looking for information (like a definition), Google won’t rank you. Successful keyword research SEO requires you to match your content type to the user’s intent.
Step 4: Analyzing the Benchmarks
Okay, so you have a list of keywords and you understand the intent. Now you need to decide which ones are actually worth your time. When you are doing keyword research SEO, you are essentially looking for a balance between three main metrics:
1. Search Volume
This is the number of times a specific keyword is searched for per month. Obviously, higher is better, but higher volume usually means higher competition.
2. Keyword Difficulty (KD)
Most SEO tools will give you a “KD” score from 0 to 100. This estimates how hard it would be to rank on the first page of Google for that term.
- If you have a brand new website, you want to target keywords with low difficulty.
- If you are an established brand, you can fight for the higher difficulty terms.
3. Relevance
Does this keyword actually apply to what you do? You might find a high-volume, low-difficulty keyword like “free hiking boots giveaway,” but if you aren’t giving away boots, targeting this would be bad keyword research SEO practice. It brings in the wrong traffic.
The Sweet Spot: You are looking for keywords with decent volume, relatively low difficulty, and high relevance.
Step 5: The Power of Long-Tail Keywords
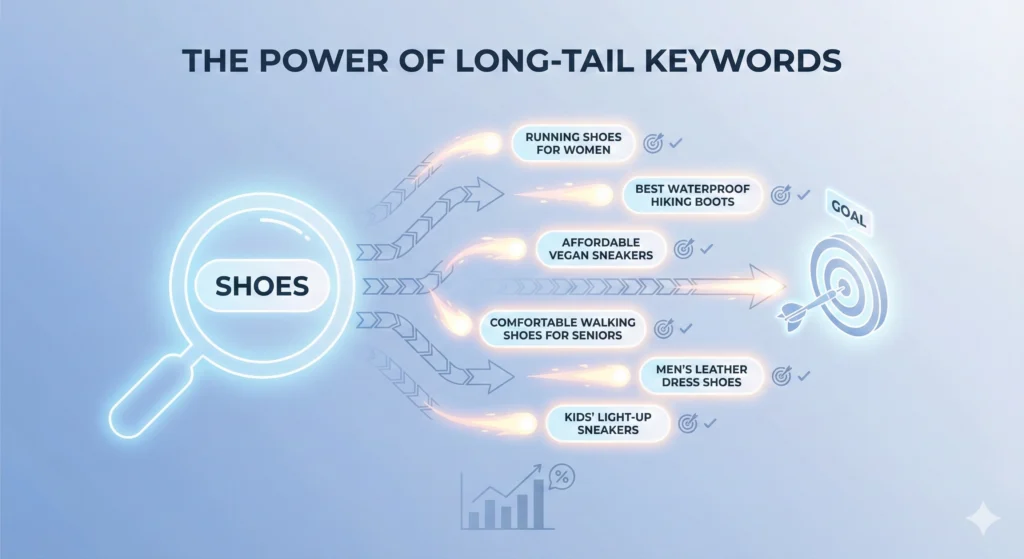
If you take one thing away from this guide, let it be this: Long-tail keywords are your best friend.
A “head” keyword is short and broad, like “shoes.” A “long-tail” keyword is specific, like “red nike running shoes for men size 10.”
Here is why long-tail keywords are the holy grail of keyword research SEO:
- Less Competition: Fewer people are trying to rank for the specific phrases.
- Higher Conversion: People searching for specific things are usually closer to making a decision.
- Clearer Intent: You know exactly what they want.
It is much easier to rank for “how to fix a broken tent zipper” than it is to rank for “tents.” When you are starting your keyword research SEO strategy, try to fill your content calendar with these specific long-tail queries. They may have lower search volume individually, but collectively, they can drive massive amounts of targeted traffic to your site.
Step 6: Spy on Your Competitors

Why reinvent the wheel when you can see what is already working? Competitor analysis is a massive part of keyword research SEO.
Go to Google and type in your seed keywords. See who ranks in the top 3 positions. Take their URLs and plug them into your SEO tool of choice. You can see exactly which keywords they are ranking for.
Look for gaps in their content.
- Is their article outdated?
- Did they miss a crucial tip?
- Is their website slow or hard to read?
If you can find a keyword that your competitor ranks for with a mediocre piece of content, that is an opportunity. You can create something better, more comprehensive, and more up-to-date. This is often called the “Skyscraper Technique,” and it relies heavily on solid keyword research SEO data to identify those weak spots in competitor content.
- You May Like: The AI-Enhanced Job Search
Step 7: Grouping and Mapping Your Keywords
You have done the hard work. You have a spreadsheet full of amazing keywords. Now, what do you do with them?
A common mistake is to try and stuff all your keywords into one post. Don’t do that. That is called “keyword stuffing,” and Google hates it.
Instead, efficient keyword research SEO involves grouping your keywords into “clusters.”
- Main Keyword: The primary topic of the page (e.g., “Best Hiking Boots”).
- Secondary Keywords: Variations and related terms (e.g., “Top rated hiking boots,” “comfortable boots for hiking”).
One page = One main intent.
Assign each keyword cluster to a specific page on your website. This is called “Keyword Mapping.” It ensures that your pages don’t compete with each other (keyword cannibalization) and that every piece of content you write has a specific search purpose.
Step 8: Creating the Content
Now we circle back to the writing. You have your keyword research SEO data mapped out. It’s time to write the blog post.
- Title Tag: Include your main keyword near the beginning.
- Headings (H1, H2, H3): Use your secondary keywords in your subheadings.
- Body Text: Use your keywords naturally. Read your text out loud. If it sounds robotic AI because you forced the keyword in, rewrite it.
- Meta Description: Include the keyword here to encourage clicks from the search results page.
Remember, keyword research SEO is just the compass; your writing is the ship. The compass points the way, but the ship needs to be sturdy (high quality) to make the journey.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even seasoned pros mess up sometimes. Here are a few pitfalls to watch out for during your keyword research SEO process:
- Ignoring Trends: Some keywords only spike during certain times (like “Christmas gift ideas”). Check the trends over 12 months.
- Focusing Only on Volume: Don’t chase the 100,000 monthly search keywords if you can’t rank for them. A keyword with 50 visits a month that actually converts customers is worth more than a vanity keyword with 10,000 visits that bounce immediately.
3.Forgetting to Update: Keyword research SEO isn’t a one-time thing. Trends change. Language changes. You need to revisit your strategy every few months to stay relevant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some of the most common questions I get asked by clients who are just starting with keyword research SEO.
1. Can I do keyword research for free? Absolutely. While paid tools like Ahrefs offer deep data, you can do effective keyword research SEO using free tools like Google Keyword Planner, Google Trends, and even the “People Also Ask” section in Google search results.
2. How often should I do keyword research? It is not a “one and done” task. You should perform fresh research every time you plan a new content campaign, or roughly every 3-6 months to spot new trends. This keeps your content strategy agile.
3. What is a “good” search volume? There is no magic number. For a niche business, a keyword with 50 searches a month might be highly profitable. For a viral news site, you might need 10,000+. In keyword research SEO, relevance is always more important than raw volume.
4. Can I target the same keyword on two different pages? You should avoid this. This causes “Keyword Cannibalization,” where your own pages compete against each other in Google rankings. Assign one primary keyword per page.
Conclusion:
Does keyword research SEO seem a little less boring now? I hope so!
At its core, it is really just about sympathy. It is about understanding what your audience is struggling with, what they are curious about, and what they need to make their lives better. When you look at the data, you aren’t just looking at numbers; you are looking at the voices of your potential customers.
By following these steps—brainstorming, using tools, understanding intent, analyzing metrics, and checking competitors—you are setting your blog up for genuine, long-term growth.
So, here is my challenge to you: Open up a blank spreadsheet right now. Write down five seed keywords for your niche. Then, go plug them into a free tool and see what comes up. You might be surprised at the opportunities waiting for you. Mastering keyword research SEO is a journey, but it’s one of the most rewarding skills you can learn in digital marketing. Happy searching!


